
[Link] https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
Using Recursive call(Top - Bottom)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return list;
lnr(root, list);
return list;
}
public void lnr(TreeNode node, List<Integer> list) {
if(node.left != null) lnr(node.left, list);
list.add(node.val);
if(node.right != null) lnr(node.right, list);
}
}
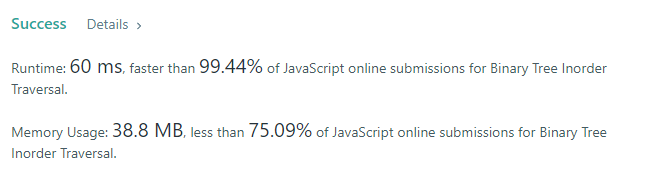
Using Stack(Bottom-Up)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
function inorderTraversal(root) {
const result = [],
stack = [];
if (root == null) return result;
stack.push(root);
topNode = root;
while (stack.length != 0) {
topNode = stack[stack.length - 1];
while (topNode.left != null && !topNode.left.visit) {
topNode = topNode.left;
stack.push(topNode);
}
topNode = stack.pop();
topNode.visit = true;
result.push(topNode.val);
if (topNode.right != null && !topNode.right.visit)
stack.push(topNode.right);
}
return result;
}
